cas/definition/feature.php (core concept)
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the study of systems that self-regulate: Adjusting their own performance to keep aligned with a pre-determined outcome, using processes of negative-feedback to help self-correct.
The word Cybernetics comes from the Greek 'Kybernetes', meaning 'steersman' or 'oarsman'. It is the etymological root of the English 'Governor'. Cybernetics is related to an interest in dynamics that lead to internal rather than external governing.
Cybernetic thought is an important early precursor to Complex Systems thinking.
Imagine a ship, sailing towards a target (say an island). There are various forces (wind and currents) that act upon the ship to push it away from its trajectory. In order to maintain a trajectory towards the island, the steersman need not be aware of the speed or direction of the wind, or the velocity of the waves. Instead, he (or she), just needs to keep their eye on the target, and keep adjusting the rudder of the ship to correct for any deviations from the route.
In a sense, we have here a complete system that works to correct for any disturbances. The system is comprised of the target, any and all forces pushing the ship away from the target, the steersman registering the amount of deviation, and subsequently counterbalancing this through means of interaction with the rudder.
While it is true that the steersman is the agent that 'activates' the rudder, it is also true that the amount of deviation the target presents also 'activates' the steersman. Finally, the forces acting upon the ship are what activates the deviation. We thus have a complete cybernetic system, where the forces at work form a continuous loop, and where the loop, in turn, is able to self-regulate.
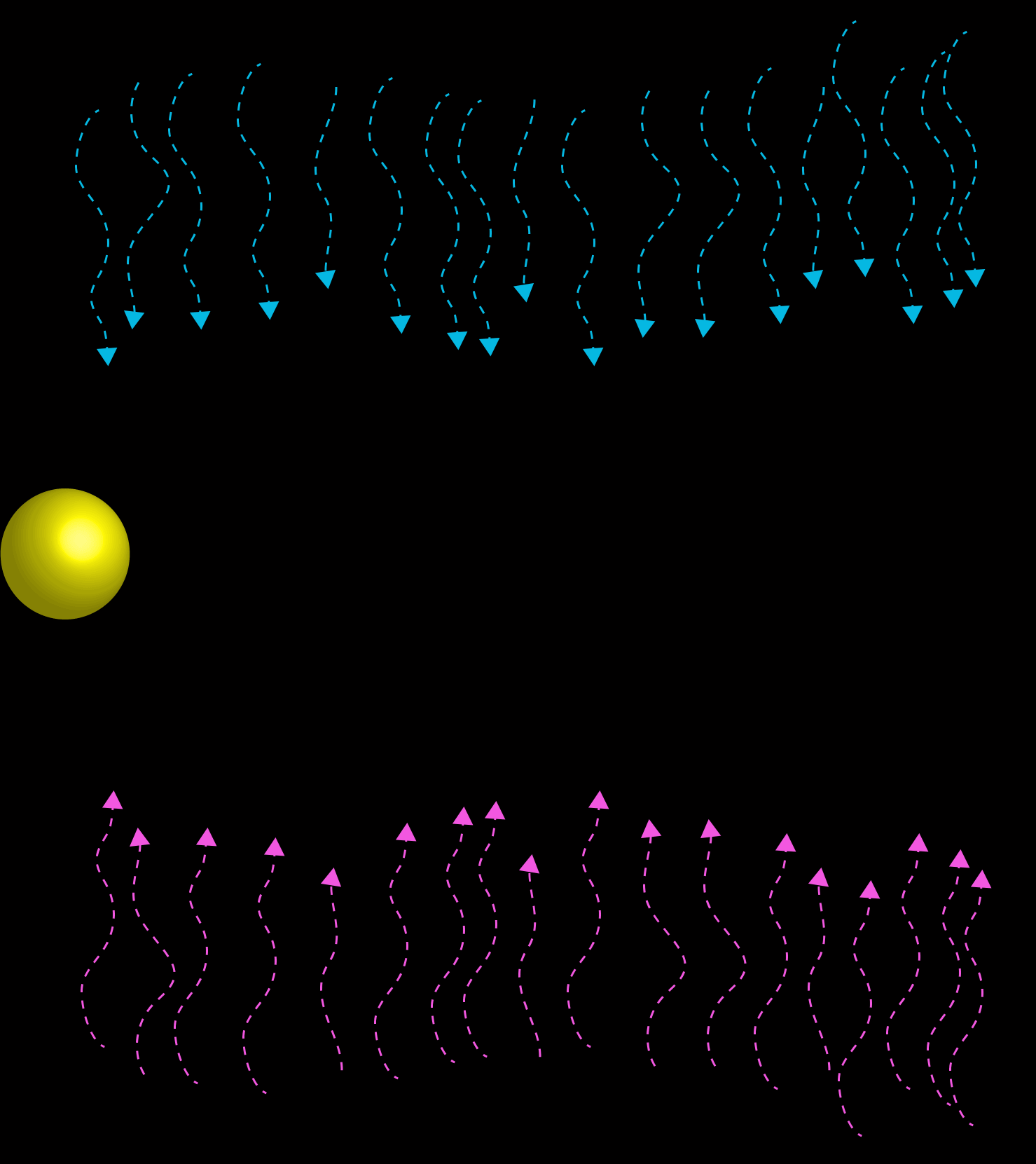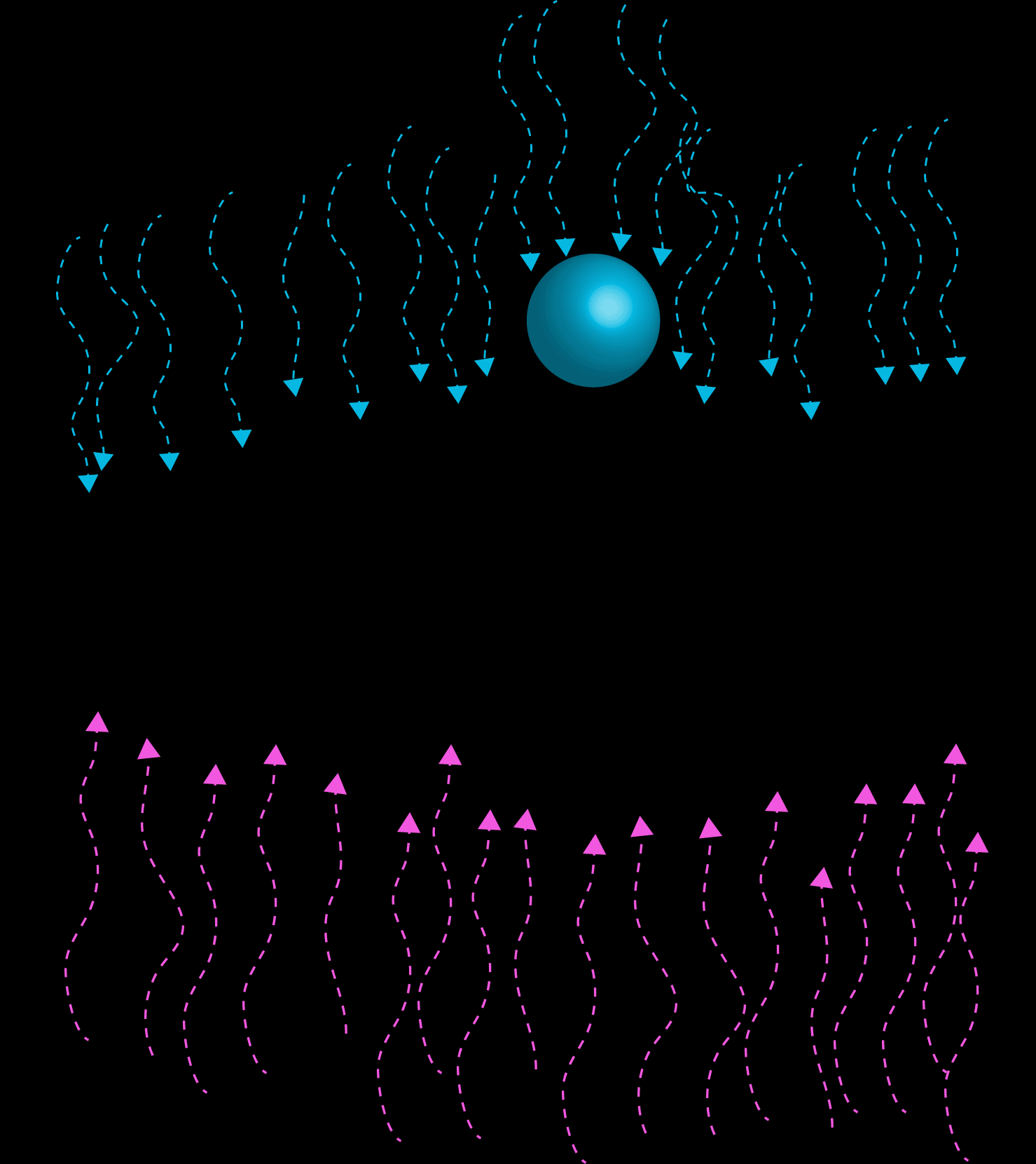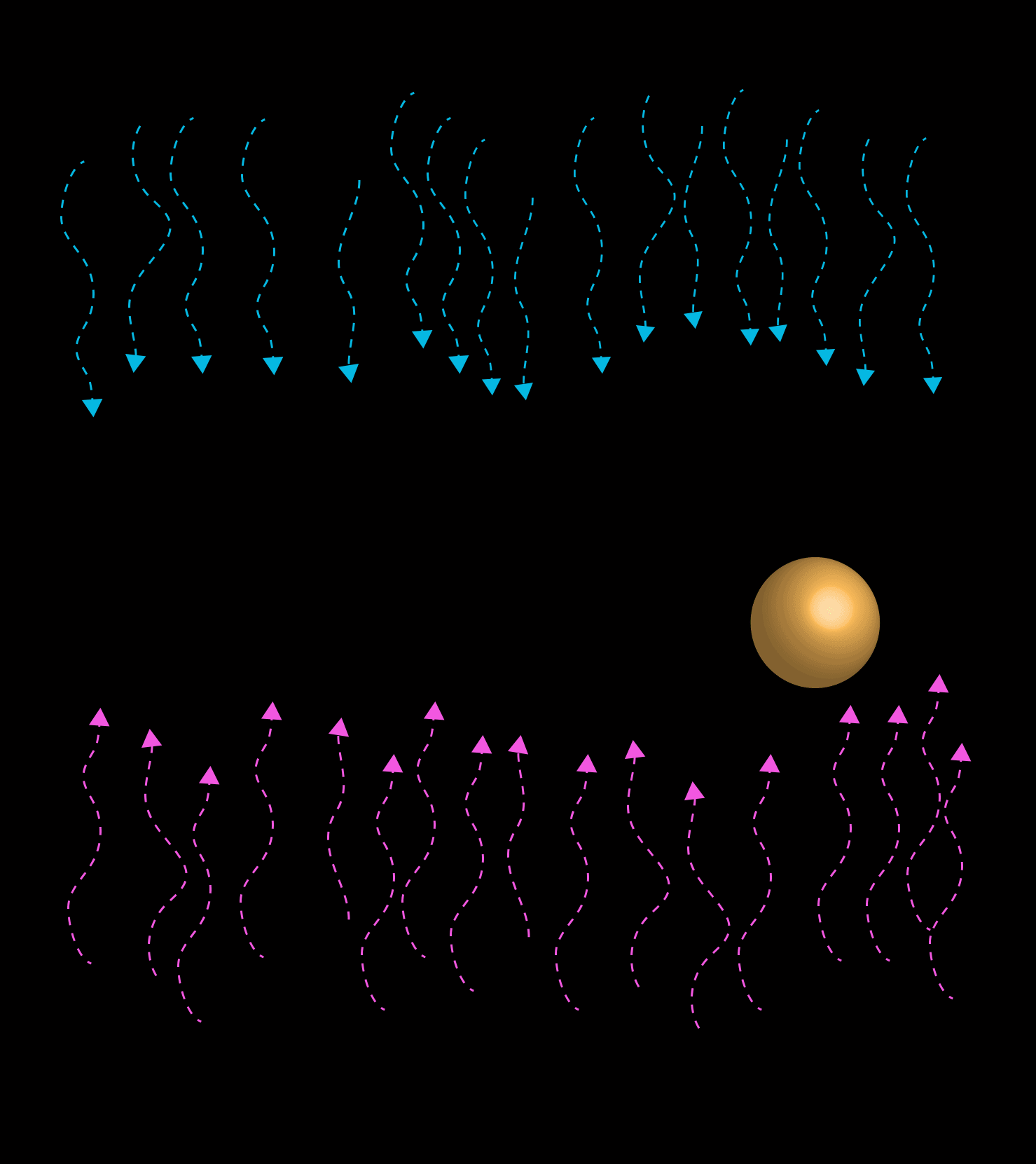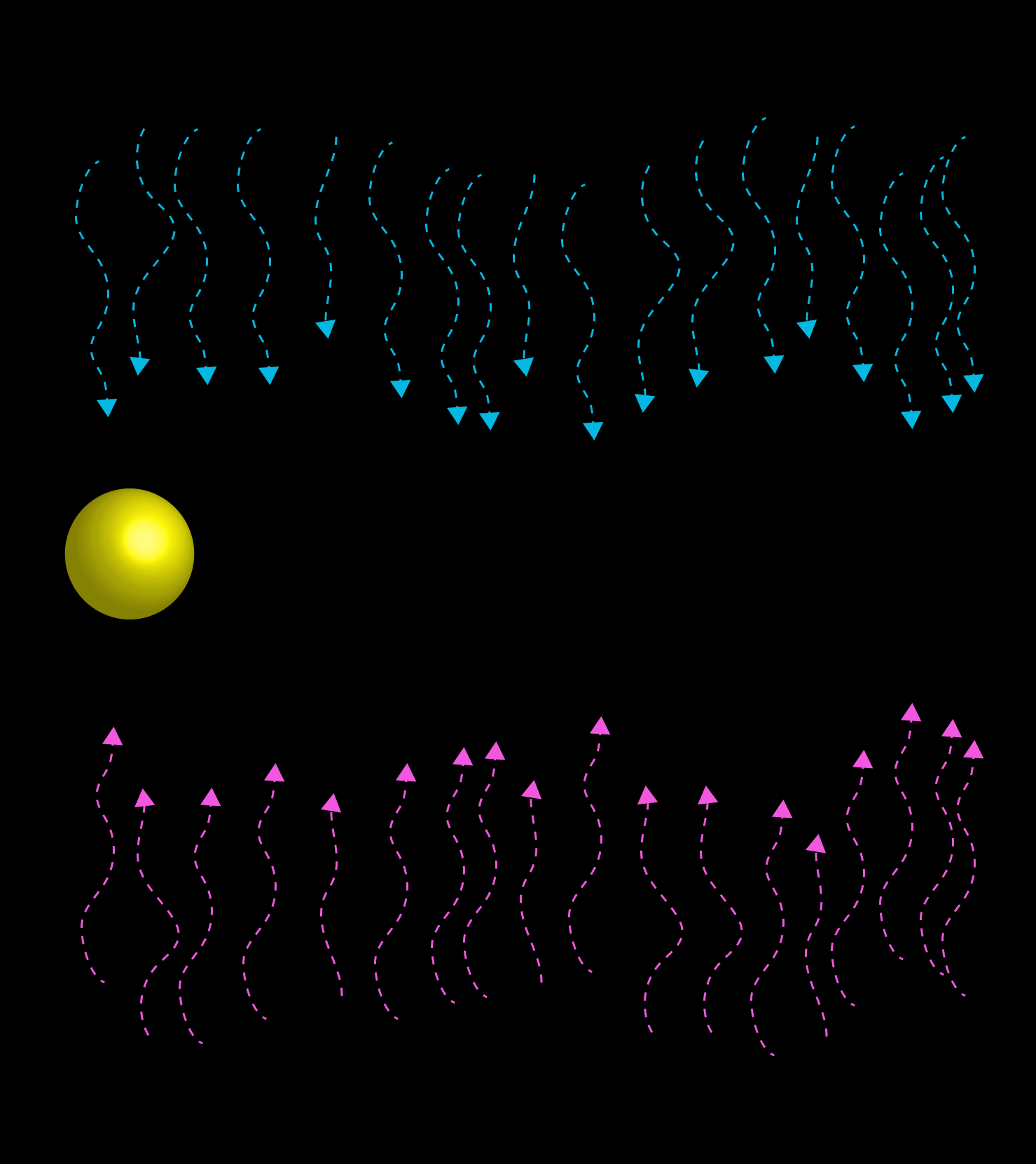
A cybernetic system works to dampen any disturbances or amplifying feedback that would move the trajectory away from a given optimum range. Thermostats work on cybernetic principles, where temperature fluctuations are dampened.
Like CAS, Cybernetics is concerned with how a system interacts with its environment. However, Cybernetics focus on systems subject to negative feedback: ones self-regulating to maintain regimes of stable equilibrium where disruptions (or Perturbations) are dampened.
Macy Conferences
Control
Stafford Beer, an early proponents of Cybernetics, discusses the Watt Flyball Regulator
Cite this page:
Wohl, S. (2022, 8 June). Cybernetics. Retrieved from https://kapalicarsi.wittmeyer.io/definition/cybernetics
Cybernetics was updated June 8th, 2022.
Nothing over here yet
This is the feed, a series of related links and resources. Add a link to the feed →
Nothing in the feed...yet.
This is a list of People that Cybernetics is related to.
Cybernetics
This is a default subtitle for this page. Learn more →General Systems Theory
This is a default subtitle for this page. Learn more →Second Order Cybernetics
This is a default subtitle for this page. Learn more →Cybernetics | Information | Differentials
This is a default subtitle for this page. Learn more →This is a list of Terms that Cybernetics is related to.
Negative Feedback is the tendency for systems to employ mechanisms whereby any fluctuations from a particular behavior or trajectory are 'dampened'; that is to say, divergence from a norm is hindered.
Negative Feedback is described in more detail on the more general {{feedback-loops}} page. Learn more →Claude Bernard
Negative Feedback | stability Learn more →This is a list of Urban Fields that Cybernetics is related to.
This is a list of Key Concepts that Cybernetics is related to.
CAS systems unfold over time, with agents continuously adjusting behaviors in response to feedback. Each iteration moves the system towards more coordinated, complex behaviors.
The concept of interactive, incremental shifts in a system might seem innocent - but with enough agents and enough increments we are able to tap into something incredibly powerful. Evolutionary change proceeds in incremental steps - and with enough of these steps, accompanied by feedback at each step, we can achieve fit outcomes. Any strategies for increasing the frequency of these iterations will further drive the effectiveness of this iterative search.
Learn more →Feedback loops occur in system where an environmental input guides system behavior, but the system behavior (the output), in turn alters the environmental context.
This coupling between input affecting output - thereby affecting input - creates unique dynamics and interdependencies between the two.
Learn more →Navigating Complexity © 2015-2025 Sharon Wohl, all rights reserved. Developed by Sean Wittmeyer
Sign In (SSO) | Sign In
Related (this page): LINKS (56), Iterations (56), Feedback (88),
Section: concepts
Non-Linearity Related (same section): Tipping Points (218, concepts), Path Dependency (93, concepts), Far From Equilibrium (212, concepts), Related (all): Urban Modeling (11, fields), Resilient Urbanism (14, fields), Relational Geography (19, fields), Landscape Urbanism (15, fields), Evolutionary Geography (12, fields), Communicative Planning (18, fields), Assemblage Geography (20, fields),
Nested Orders Related (same section): Self-Organized Criticality (64, concepts), Scale-Free (217, concepts), Power Laws (66, concepts), Related (all): Urban Modeling (11, fields), Urban Informalities (16, fields), Resilient Urbanism (14, fields),
Emergence Related (same section): Self-Organization (214, concepts), Fitness (59, concepts), Attractor States (72, concepts), Related (all): Urban Modeling (11, fields), Urban Informalities (16, fields), Urban Datascapes (28, fields), Incremental Urbanism (13, fields), Evolutionary Geography (12, fields), Communicative Planning (18, fields), Assemblage Geography (20, fields),
Driving Flows Related (same section): Open / Dissipative (84, concepts), Networks (75, concepts), Information (73, concepts), Related (all): Urban Datascapes (28, fields), Tactical Urbanism (17, fields), Relational Geography (19, fields), Parametric Urbanism (10, fields), Landscape Urbanism (15, fields), Evolutionary Geography (12, fields), Communicative Planning (18, fields), Assemblage Geography (20, fields),
Bottom-up Agents Related (same section): Rules (213, concepts), Iterations (56, concepts), Related (all): Urban Modeling (11, fields), Urban Informalities (16, fields), Resilient Urbanism (14, fields), Parametric Urbanism (10, fields), Incremental Urbanism (13, fields), Evolutionary Geography (12, fields), Communicative Planning (18, fields),
Adaptive Capacity Related (same section): Feedback (88, concepts), Degrees of Freedom (78, concepts), Related (all): Urban Modeling (11, fields), Urban Informalities (16, fields), Tactical Urbanism (17, fields), Parametric Urbanism (10, fields), Landscape Urbanism (15, fields), Incremental Urbanism (13, fields), Evolutionary Geography (12, fields),
